Saxenda® is approved for adolescents aged 12 to 17 with obesity3
You can help them with Saxenda®, a GLP-1 receptor agonist to help weight management in adolescents, used along with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.3a And knowing what to look for can help you connect adolescents with treatment sooner.
aBased on a 56-week adolescent trial.


Goal:
Wants to get to a healthier weight before starting high school and trying out for the football team in the fall
History:
Enjoys playing sports and has a family history of obesity
Previous weight-loss attempts:
Lost weight last summer after starting football camp and limiting junk food, but gained it back steadily once the school year started
Primary End Point

The observed mean change in BMI SDS from baseline was
-0.23 with Saxenda® (baseline=3.14) and -0.00 with placebo (baseline=3.2)3,4
(ETD: -0.22; 95% CI: -0.37, -0.08; p=0.0022)3,4
Supportive Secondary End Point

Compared with those using healthy nutrition and physical activity counseling alone (baseline=102.2 kg), adolescents saw reductions in body weight with Saxenda® (baseline=99.3 kg).3
BMI SDS, body mass index standard deviation score.
ETD, estimated treatment difference.

Supportive Secondary End Point

Estimated mean relative change in body weight (%) from baseline3,4
Baseline=99.3 kg for Saxenda® and 102.2 kg for placebo


Study Design
The effect of Saxenda® in adolescent patients was compared with placebo in a 56-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study of 251 pubertal patients aged 12 to 17 years with a BMI corresponding to ≥30 kg/m2 for adults by international cutoff points and BMI of ≥95th percentile for age and sex. Both groups received lifestyle therapy, consisting of healthy nutrition and physical activity counseling for weight loss.3,4
After a 12-week lifestyle run-in period, patients were randomized 1:1 to Saxenda® once daily or placebo once daily. The Saxenda® dose was titrated to 3 mg over a 4- to 8-week period based on tolerability.3 The primary end point was change in BMI SDS. Select supportive secondary end points included change in body weight.3,4
Saxenda® demonstrated statistically significant reduction in BMI SDS3,4
- BMI SDS, also known as z-score, tells you the number of standard deviations an adolescent is from the population mean BMI matched for age and gender4,5
- Due to growth during childhood and adolescence, BMI values alone cannot be used to assess efficacy5,6
- BMI SDS reductions of at least 0.20 are considered clinically meaningful5
An established safety and tolerability profile
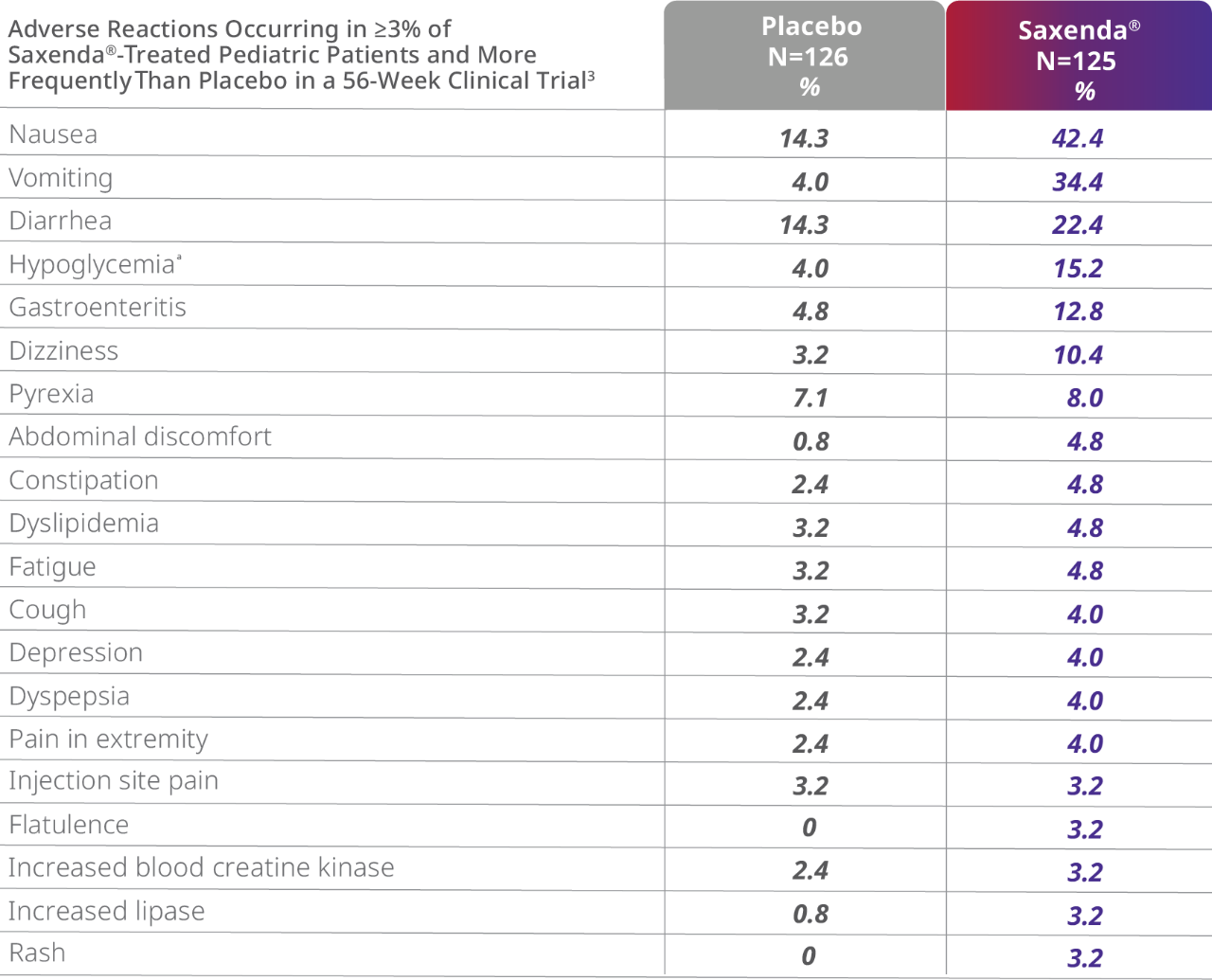

aDefined as blood glucose <70 mg/dL with symptoms of hypoglycemia. Pediatric patients did not have type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- 8% of patients taking Saxenda® vs 0% taking placebo discontinued treatment as a result of gastrointestinal adverse events3
- Gastrointestinal adverse events occurred primarily during the dose-escalation period and diminished over time4
- 1 death due to suicide in a patient treated with Saxenda® occurred in the trial3
- 1 patient (0.8%) treated with Saxenda® experienced pancreatitis3
- More episodes of hypoglycemia occurred in patients taking Saxenda® (1.6%) vs placebo (0.8%)3
- Mean increases in resting heart rate of 3 to 7 beats per minute from baseline were observed with patients taking Saxenda®3
In addition to the clinical trial in adolescents, Saxenda® has been evaluated for safety in 5 clinical trials with 3,384 adults.3
Titration to help with tolerability
Patients should follow a 4-week dosage escalation to reach the clinically efficacious 3 mg dosage.


Patients who do not tolerate 3 mg daily may have their maintenance dose reduced to 2.4 mg daily. Discontinue Saxenda® if the patient cannot tolerate the 2.4 mg dose. If patients cannot tolerate an increased dosage during dosage escalation, consider lowering the dosage to the previous level. Dosage escalation could take up to 8 weeks.3
Evaluate the change in BMI after 12 weeks on the maintenance dose and discontinue Saxenda® if the patient has not had a reduction in BMI of at least 1% from baseline, since it is unlikely that the patient will achieve and sustain clinically meaningful weight loss with continued treatment.3
Important Safety Information for Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether Saxenda® causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Saxenda® is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC with use of Saxenda® and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (eg, a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Saxenda®.
Indications and Usage
Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg is indicated as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in:
- Adult patients with an initial body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or greater (obese) or 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition (eg, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia)
- Pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with body weight above 60 kg (132 lbs) and initial BMI corresponding to 30 kg/m2 or greater for adults (obese) by international cut-offs
Limitations of Use
- Saxenda® contains liraglutide and should not be coadministered with other liraglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes have not been established
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in combination with other products intended for weight loss, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal preparations, have not been established
Important Safety Information cont.
Contraindications
Saxenda® is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a personal or family history of MTC or patients with MEN 2
- Patients with a serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or to any of the excipients in Saxenda®. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with Saxenda®
- Pregnancy
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors: If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated
- Acute Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with liraglutide postmarketing. Observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis (persistent severe abdominal pain, sometimes radiating to the back with or without vomiting). If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue Saxenda® promptly and if pancreatitis is confirmed, do not restart
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: Substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis; however, the incidence of acute gallbladder disease was greater in patients treated with Saxenda® than with placebo even after accounting for the degree of weight loss. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated
- Hypoglycemia: Adult patients with type 2 diabetes on an insulin secretagogue (eg, a sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia with use of Saxenda®. The risk may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of insulin secretagogues or insulin. In pediatric patients without type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia occurred. Inform all patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms
- Heart Rate Increase: Mean increases in resting heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute (bpm) were observed in patients treated with Saxenda®. Monitor heart rate at regular intervals and inform patients to report palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during treatment with Saxenda®. Discontinue Saxenda® in patients who experience a sustained increase in resting heart rate
- Renal Impairment: Acute renal failure and worsening of chronic renal failure, which may sometimes require hemodialysis, have been reported, usually in association with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or dehydration. Use caution when initiating or escalating doses of Saxenda® in patients with renal impairment
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis and angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with Saxenda®. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, patients should stop taking Saxenda® and promptly seek medical advice
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: In adult clinical trials, 9 (0.3%) of 3,384 patients treated with Saxenda® and 2 (0.1%) of the 1,941 treated with placebo reported suicidal ideation; one of the Saxenda® treated patients attempted suicide. In a pediatric trial, 1(0.8%) of the 125 Saxenda® treated patients died by suicide. There was insufficient information to establish a causal relationship to Saxenda®. Monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue treatment if patients experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Avoid Saxenda® in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Saxenda® delays gastric emptying. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking Saxenda®
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions, reported in ≥5% are nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, injection site reactions, headache, hypoglycemia, dyspepsia, fatigue, dizziness, abdominal pain, increased lipase, upper abdominal pain, pyrexia, and gastroenteritis
Drug Interactions
- Saxenda® causes a delay of gastric emptying and has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Monitor for potential consequences of delayed absorption of oral medications concomitantly administered with Saxenda®
Use in Specific Populations
- There are no data on the presence of liraglutide in human breast milk; liraglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats
- Saxenda® has not been studied in patients less than 12 years of age
- Saxenda® slows gastric emptying. Saxenda® has not been studied in patients with preexisting gastroparesis
Please click here for Saxenda® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
References
1. Lifshitz F. Obesity in children. J Clin Res Ped Endo. 2008;1(2):53-60.
2. Gordon-Larsen P, The NS, Adair LS. Longitudinal trends in obesity in the United States from adolescence to the third decade of life. Obesity. 2010;18(9):1801-1804.
3. Saxenda® [package insert]. Plainsboro, NJ: Novo Nordisk Inc.; 2022.
4. Kelly AS, Auerbach P, Barrientos-Perez M, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of liraglutide for adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2117-2128.
5. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: US Preventative Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. US Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2417-2426.
6. European Medicines Agency. Guideline on clinical evaluation of medicinal products used in weight control: addendum on weight control in children. Published August 7, 2016. Accessed July 14, 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/clinical-evaluation-medicinal-products-used-weight-control